Why is it Necessary to Dry Grains Before Storage?

Throughout agricultural history, grain has served as a fundamental resource, playing a vital role in food security, economic prosperity, and cultural significance. However, the journey of grain from the field to our tables is significantly influenced by post-harvest handling, especially the process of drying grains before storage. This article explores in detail why drying grains is imperative, providing comprehensive insights into the benefits, methods, and best practices in maintaining grain quality and safety.
The Importance of Drying Grains
Grains such as wheat, corn, rice, and barley are staple foods worldwide. Hence, understanding the significance of their proper storage is crucial. Below are some key reasons underscoring the necessity to dry grains:
- Prevention of Mold and Fungal Growth: Moist grains provide a perfect environment for mold spores and fungi to thrive. High moisture content can lead to mycotoxin contamination, making the grain unsafe for consumption.
- Blockage of Insect Infestation: Insects such as weevils are attracted to high-moisture grains. Drying grains effectively reduces moisture levels, discouraging pest infestations that can cause significant losses.
- Optimization of Storage Conditions: Drier grains store better over prolonged periods. They reduce the risk of spoilage, thus ensuring that farmers and businesses maximize their investments.
- Maintaining Nutritional Quality: Properly dried grains preserve their nutritional integrity, preventing the loss of vitamins and minerals that can occur with improper storage conditions.
- Enhancing Market Value: Grain with optimal moisture content is more appealing in the marketplace. It helps fetch higher prices, ensuring better profitability for farmers and suppliers.
Understanding Moisture Content in Grains
Moisture content is defined as the percentage of water in the grain relative to its total weight. For instance, freshly harvested grains may have moisture contents that exceed 20%. However, the ideal moisture content for long-term storage typically ranges from 12% to 14%, varying by grain type. Here are a few common types of grains and their recommended moisture levels:
- Wheat: Ideal moisture content of 12-14%
- Corn: Ideal moisture content of 13-15%
- Barley: Ideal moisture content of 12-14%
- Rice: Ideal moisture content of 14-15%
Monitoring this moisture content is essential since it directly affects the grain's quality, storage longevity, and usability.
Methods of Drying Grains
Grain drying can be accomplished through various methods, each with its unique advantages and applicable contexts. Below are some of the most common methods:
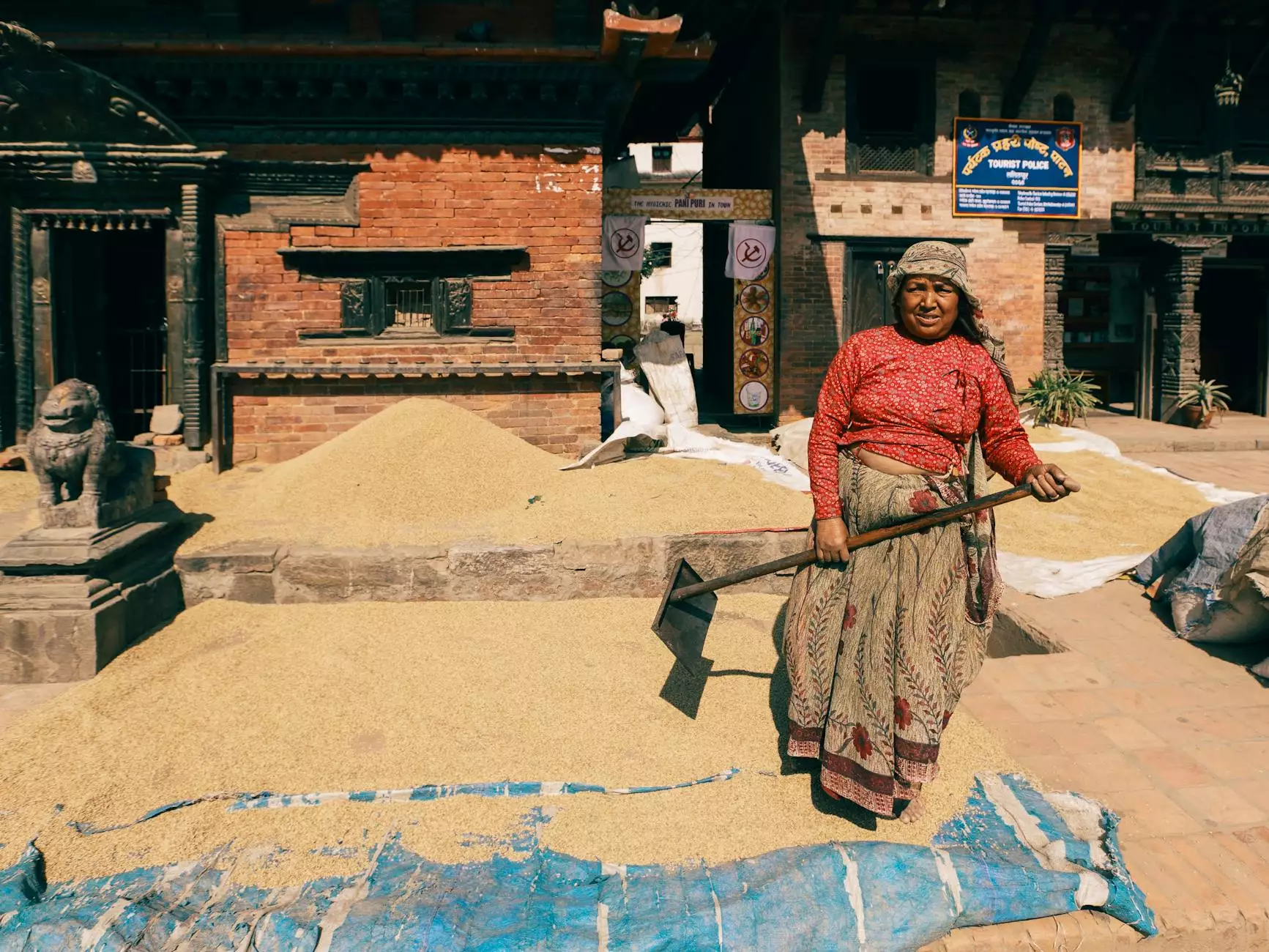
1. Natural Sun Drying
Natural sun drying involves spreading harvested grains in a thin layer under sunlight. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, but it is highly dependent on favorable weather conditions.
Advantages:
- Low operational cost
- No requirement for sophisticated equipment
- Preservation of the grain's natural qualities
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming
- Vulnerability to weather changes Risk of pest and rodent attacks
2. Mechanical Drying
Mechanical drying utilizes specialized equipment such as grain dryers to hasten the drying process. This method is more controlled and efficient, allowing grain to dry uniformly.
Advantages:
- Quick and efficient drying process
- Lower risk of grain degradation
- Ability to control drying parameters precisely
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial investment
- Operational costs for fuel or electricity
3. Heated Air Drying
In heated air drying, hot air is circulated through the grains, removing moisture effectively. This method can be used with mechanical dryers to speed up the drying process.
Advantages:
- Reduces drying time significantly
- Minimizes risks associated with spoilage
Disadvantages:
- Potential for thermal damage if not monitored
- Higher energy consumption
4. Vacuum Drying
Vacuum drying is a sophisticated technique that removes moisture from grain under reduced pressure. This method can help maintain the grain's nutritional quality and flavor.
Advantages:
- Preservation of bioactive compounds
- Lower drying temperatures minimize damage
Disadvantages:
- High cost and complexity
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise
Best Practices for Drying and Storing Grains
To ensure the effectiveness of grain drying techniques, a systematic approach is necessary. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Regular Monitoring
Establish a routine for checking moisture levels, employing moisture meters as necessary. This regularity aids in determining when grains reach optimal dryness.
2. Proper Ventilation
Ensuring adequate airflow during drying is crucial. Proper ventilation minimizes the risk of hot spots that can lead to mold growth.
3. Clean Storage Facilities
Before storing dried grains, ensure that storage facilities are clean and free from previous grain residues that may harbor pests and pathogens.
4. Use Appropriate Storage Containers
The choice of storage containers impacts grain safety. Use grain bins or silos made of moisture-resistant materials to safeguard grain integrity.
5. Monitoring Temperature and Humidity
Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels within storage facilities enhances durability and usability. Employ automatic climate control systems if necessary.
The Economic Impact of Proper Grain Drying
Beyond the direct benefits to grain quality, adequate drying techniques translate to economic advantages for farmers and businesses:
- Reduction in Post-Harvest Losses: Efficient drying minimizes grain loss due to spoilage and pest infestations, providing a better return on investment.
- Improved Marketability: Dried grains maintain their quality, positioning farmers favorably in the marketplace and potentially enhancing profits.
- Lower Processing Costs: Grains stored in optimal conditions require less processing and sorting, reducing operational costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of why is it necessary to dry grains before storage is pivotal for anyone involved in agriculture, grain handling, or marketing. Through the prevention of spoilage, pest damage, and nutritional degradation, drying grains is not just a best practice; it is an essential process that guarantees safety, quality, and economic benefits in the long run. Implementing the right drying methods and adhering to best practices will ensure that grains maintain their value, contributing to a sustainable agricultural future.
For expert assistance in farm equipment repair and advice on maintaining your farming equipment to enhance the grain drying process, visit TSGC Inc. today.